 The Indian technical textiles sector has immense potential to grow both domestically as well as globally. Backed by government initiatives and support, India can emerge as a global manufacturing hub for technical textiles in the future.
The Indian technical textiles sector has immense potential to grow both domestically as well as globally. Backed by government initiatives and support, India can emerge as a global manufacturing hub for technical textiles in the future.
It is a massive market that remains overshadowed by its conventional cousin. And, all discussion about its scope remains confined mostly to stakeholders. But almost unnoticed-certainly by those not conversant with the sector—technical textiles have already emerged from the shadow of the overall textiles industry and is now reckoned to be an entity of its own. Plus, it is big.
The global technical textiles market was valued at $157.68 billion in 2016 and is projected to reach $220.37 billion by 2022 at a CAGR of 5.89 per cent from 2017, according to a recent report by Markets and Markets. The major factors driving this market are growing demand and government initiatives in promoting this sector. The increasing use of technical textiles in end-use industries such as automobiles, construction, healthcare and geotextiles too are driving the market. The technical textiles used in these industries is being attributed to the unique function properties—hygiene and safety, cost-effectiveness, durability, strength, versatility, user-friendliness, lightweight and logistical convenience.
Back home, the growth drivers of the Indian technical textiles markets include:
Growing industrialisation,
Changing lifestyles,
Improvement in safety and hygiene,
Increase in technology, and
Awareness of protective wear.
The Indian market
The Indian technical textiles sector is growing along with that of the end-user industries. The sectorcontributes around 12 per cent to the overall Indian textiles market. The major factor contributing to the growth of Indian technical textiles are infrastructure and industrial development in the country.
Government initiatives too are attracting investments. The government has put in place the following policies to develop a comprehensive manufacturing base for high-value technical textiles in India.
Export Promotion of Capital Goods (EPCG),
Amended Technological Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS),
Schemes for agro-textile usage in the Northeast region,
Scheme for the usage of geotechnical textiles in the Northeast,
Benefits under Special Economic Zone (SEZ) and Schemes for Integrated Textile Parks (SITP).
Domestic consumption has increased by 6.8 per cent in recent years. To make the Indian technical textiles industry competitive globally, a dual policy needs to be adopted for exports as well as domestic markets. The industry is expected to expand at CAGR of 13.11 per cent during 2018–23 to $32 billion.
Exports and imports
India is a net exporter of technical textile products, with exports touching $1,849.8 million in 2017–18. Exports will grow at a CAGR of 3.3 per cent in the five years. After two consecutive years of decline, exports recovered remarkably in 2017–18 to register a significant y-o-y growth of 18.4 per cent, increasing from $1,562.5 million in the previous year to $1,849.8 million in 2017–18.
The US was the leading destination with exports estimated at $336.8 million in 2017-18. The value of US exports recorded a healthy CAGR of 10.6 per cent in the period between 2013–14 and 2017–18. The US share in Indian exports of technical textiles increased from 13.9 per cent to 18.2 per cent in the period.
Imports of technical textile products ($1,744.8 million) increased substantially in 2017–18 at a growth rate of 21.7 per cent. Imports recorded a CAGR of 8.1 per cent between 2013–14 and 2017–18.
The largest import source of technical textile products was China, accounting for more than 50 per centshare in both 2013–14 and 2017–18. The value of imports from China recorded a CAGR of 8.2 per cent in those four years. Other major import sources in 2017–18 included Thailand, Taiwan, the US, Bangladesh, Germany, South Korea, Malaysia, Hong Kong and Nepal.
Growth as global manufacturer
India should grow as a global technical textiles manufacturing hub with the following advantages:
Extensive availability of textile raw material;
Technical textiles being a labour-intensive industry, the presence of a large pool of labour at a comparatively low cost can provide a competitive edge over technical textile producing countries like China, the US, and those in Europe;
Power costs are lower than other countries, and lending rates are higher than in China and Vietnam; with government schemes, the effective cost of capital becomes comparable;
India’s infrastructure for technical textiles is developing with investment in R&D, testing and investor facilitation from the Centre of Excellence.
Even though the global industry is dominated by European countries and China, there is potential in India to emerge as a global manufacturing hub for technical textiles in the future.
Steps needed to grow further
Indian government schemes for textiles and apparel manufacturers have been targeting technology up-gradation, infrastructure development, export promotion and many more segments. State governments should also announce their own policies for attracting investors to their respective states.
However, India is yet to exploit its potential in technical textiles sector due to reasons such as the absence of regulatory measures for technical textile usage in various industries. Moreover, the country is still dependent on imports for technology and advanced machinery and India has limited production of high-end products and specialized yarns and intricate duty structure.
To facilitate the growth of the Indian technical textiles industry, several measures need attention. Some of them are:
Establishing regulatory norms to increase the consumption of technical textile goods;
Developing exclusive HSN codes to identify high growth products for further development;
Establishing and implementing Indian standards to develop high-quality products for global acceptance;
Better operational standards;
Focus on training, education and creating end-user awareness to boost domestic demand for high-end technical textile products.
Besides this, India should also focus on forming partnerships with other global payers for acquiring technical know-how. This will help the country to attract large-scale investments.

 Are you ready for personal interview of NIFT MFM/MDes/M.FTech Like last year,NIFT has announced to conduct Personal Interview only for MFM/MDes/MFtech program due to Pandemic . Now let’s understand what is PI round for NIFT Master program. It is all about judging candidate’s over all personality, Knowledge about Industry and his keen interest in respective course for which She/He has been shortlisted. To understand and get an idea about PI ,Join Mock PI session with PAHAL DESIGN in order to robust your preparation for NIFT PI round. Book your slot -> Also Call 📞880022-6864
Are you ready for personal interview of NIFT MFM/MDes/M.FTech Like last year,NIFT has announced to conduct Personal Interview only for MFM/MDes/MFtech program due to Pandemic . Now let’s understand what is PI round for NIFT Master program. It is all about judging candidate’s over all personality, Knowledge about Industry and his keen interest in respective course for which She/He has been shortlisted. To understand and get an idea about PI ,Join Mock PI session with PAHAL DESIGN in order to robust your preparation for NIFT PI round. Book your slot -> Also Call 📞880022-6864









 How to prepare for NIFT MFM, M.Des , M.Ftech group discussion
How to prepare for NIFT MFM, M.Des , M.Ftech group discussion Fashion and Animation tops comparative student enrollment within design. Animation is growing at a very fast rate primarily for two reasons. The first reason is establishment of animation as a viable career option and second being the abundance availability of animation education in cities of all sizes. Similarly for Fashion Design it is the availability of instruction in this area in all geographies. Fashion and Animation has seen a tremendous growth in urban and semi urban areas where institutes are offering certificate and diploma courses ranging from 3 months duration to 2 years. Many of these institutes are franchises of major institutes. Fashion Design is offered as a 3 year / 4 year Bachelors Degree program by many universities and is also offered as a 3 year diploma course post 10 years of school education.
Fashion and Animation tops comparative student enrollment within design. Animation is growing at a very fast rate primarily for two reasons. The first reason is establishment of animation as a viable career option and second being the abundance availability of animation education in cities of all sizes. Similarly for Fashion Design it is the availability of instruction in this area in all geographies. Fashion and Animation has seen a tremendous growth in urban and semi urban areas where institutes are offering certificate and diploma courses ranging from 3 months duration to 2 years. Many of these institutes are franchises of major institutes. Fashion Design is offered as a 3 year / 4 year Bachelors Degree program by many universities and is also offered as a 3 year diploma course post 10 years of school education. Q. How was the NIFT 2021 Exam? Was it lengthy, difficult or moderate? What’s your analysis of the exam?
Q. How was the NIFT 2021 Exam? Was it lengthy, difficult or moderate? What’s your analysis of the exam?

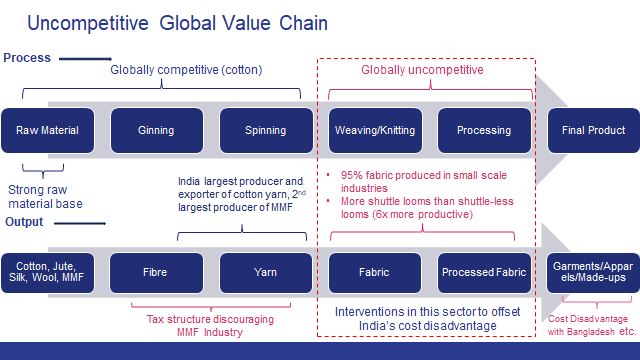
 While India leads in cotton yarn exports, it has been a very marginal player when it comes to cotton fabric in world exports. China has a substantial share of 51% in cotton fabrics when compared to India’s 5%–6%; the situation is almost the same in case of MMF fabrics. This comparison suggests that India is not able to scale up the value chain significantly enough to meet the global demand despite being the largest producer and exporter of cotton yarn.
While India leads in cotton yarn exports, it has been a very marginal player when it comes to cotton fabric in world exports. China has a substantial share of 51% in cotton fabrics when compared to India’s 5%–6%; the situation is almost the same in case of MMF fabrics. This comparison suggests that India is not able to scale up the value chain significantly enough to meet the global demand despite being the largest producer and exporter of cotton yarn.